해당 강의를 듣고 정리한 것입니다
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/9
자바 중급
평가 5.0 17개의 평가 ★★★★★17 ★★★★0 ★★★0 ★★0 ★0 ds02168 2021.08.20 15:37 Yeonggwang 2021.06.28 01:48 강신우 2021.04.23 10:20 HyeonWoo Jeong 2021.04.08 17:12 이용준 2021.01.26 19:23 리뷰 더보기
programmers.co.kr
스레드와 상태 제어
: 스레드가 3개가 있다면 JVM은 시간을 잘게 쪼갠 후 한 번은 스레드 1을, 한 번을 스레드 2를, 한 번은 스레드 3을 실행합니다. 이것을 빠르게 진행하다 보니 모두 동작하는 것처럼 보이는 것.
- 스레드는 실행 가능 상태인 Runnable과 실행상태인 Running상태로 나뉨
- 실행되는 스레드 안에서 Thread.sleep()이나 Object가 가지고 있는 wait() 메서드가 호출이 되면 스레드는 블록 상태
- Thread.sleep()은 특정 시간이 지나면 자신 스스로 블록 상태에서 빠져나와 Runnable이나 Running상태 전환
- Object가 가지고 있는 wait() 메서드는 다른 스레드가 notify()나 notifyAll() 메서드를 호출하기 전까진 블록 상태에서 해제되지 않음
- wait() 메서드는 호출이 되면 모니터링 락을 놓게 되어 다른 대기 중인 메서드가 실행
- 스레드의 run메서드가 종료되면, Dead상태로 전환(스레드 종료)
- Thread의 yeild메서드가 호출되면 해당 스레드는 다른 스레드에게 자원을 양보
(양보받은 스레드의 실행 속도를 높이기 위해 사용) - Thread가 가지고 있는 join메서드를 호출하게 되면 해당 스레드가 종료될 때까지 대기
- main메서드 또한 하나의 메서드
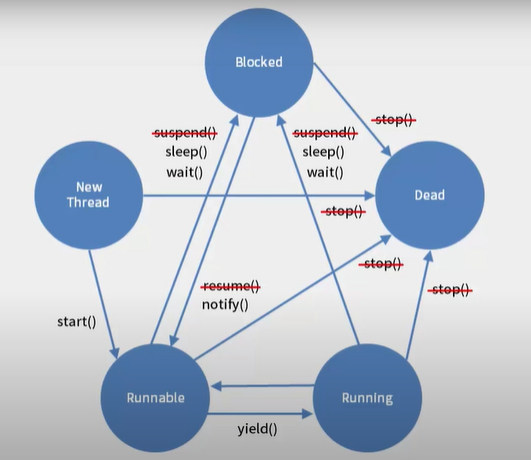
(빨간 줄이 그어져 있는 메서드들은 deprecated 된 것들!!! 사용을 자제하자)
Join()
: join() 메서드는 스레드가 멈출 때까지 기다리게 함
- 0.5초씩 쉬면서 숫자를 출력하는 MyThread5
public class MyThread5 extends Thread{
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
System.out.println("MyThread5 : " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
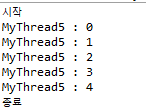
}- 해당 스레드를 실행하고, 해당 스레드가 종료될 때까지 기다린 후, 내용을 출력하는 JoinExam클래스
public class JoinExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread5 thread = new MyThread5();
thread.start();
System.out.println("시작");
try {
thread.join();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("종료");
}
}실행결과
wait(), notify()
: Object의 메서드!
wait와 notify는 동기화된(synchronized) 블록 안에서 사용해야 한다.
wait을 만나게 되면 해당 스레드는 모니터링 락에 대한 권한을 놓고 대기한다!
하나만 wait 시켰을 때는 괜찮지만 여러 개가 있을 때는 notify() 시 어떤 객체가 깨어날지 모르기떄문에 notfiAll()로 모든 객체를 깨운 뒤 JVM의 스레드 스케쥴링에 의해서 처리되는 것이 안전하다고 한다
- Thread를 상속받는 ThreadB클래스 작성
public class ThreadB extends Thread{
int total;
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
System.out.println(i+"를 더합니다");
total += i;
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
notify();
}
}
}- ThreadB를 사용해 wait 하는 클래스 작성
public class ThreadA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadB b = new ThreadB();
b.start();
synchronized (b) {
try {
System.out.println("b가 완료될때까지 기다림.");
b.wait();
System.out.println("total is : "+ b.total);
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}실행결과

해당 코드의 synchronized 블록 내부
- main스레드가 System.out.println("b가 완료될 때까지 기다림."); 문장 실행 후
- b.wait();을 만나 main스레드는 대기한다.
- b.run() 메서드 끝에 notify();가 있기 때문에 main스레드의 대기를 풀어줌
(notify();를 해주지 않아도 b스레드가 끝나면 main스레드가 시작됨!) - 대기가 풀렸기 때문에 System.out.println("total is : " + b.total); 문장이 실행된다.
데몬 스레드(Daemon)
: 데몬(Daemon) : 리눅스 같은 유닉스 계열의 운영체제에서 백그라운드로 동작하는 프로그램(window는 서비스)
- 데몬스 레드를 만드는 방법은 스레드에 데몬 설정을 하면 된다.
- 해당 스레드는 자바 프로그램을 만들 때 백그라운드에서 특별한 작업을 처리하게 하는 용도 - 데몬스 레드는 일반 스레드(main 등)가 모두 종료되면 강제적으로 종료되는 특징이 있다!!
public class DaemonThread implements Runnable{
public void run() {
while(true) {
System.out.println("데몬 스레드가 실행중.");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new DaemonThread());
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("메인 스레드가 종료됨.");
}
}실행결과

'Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자바 코딩테스트를 위한 정리 - 입출력 (0) | 2022.05.10 |
|---|---|
| 자바 중급17 : 람다(lambda) (0) | 2022.01.19 |
| 자바 중급15 - 스레드(쓰레드, Thread) 1 : 생성, 공유객체, 동기화블록(Snchronized) (0) | 2022.01.19 |
| 자바 중급14 - 어노테이션(Annotation) (1) | 2022.01.19 |
| 자바 중급13 - 자바IO (0) | 2022.01.18 |