반응형
프로토 타입 패턴이란?
- 객체를 생성할 때 기존 객체를 복제하여 새로운 객체를 생성하는 방법을 제공하는 패턴이다. 이를 통해서 객체의 복잡한 생성 과정을 피하고, 기존 객체의 상태를 유지하며 새로운 객체를 생성할 수 있게 된다.
- 프로그래밍에서 변경이 일어나는 부분을 캡슐화한다는 따른다.
왜 사용하나요?
- 객체 생성 과정이 복잡하거나 시간이 많이 걸릴 경우, 기존 객체를 복제하여 새로운 객체를 생성하는 것이 효율적이기 때문이다.
- 객체의 클래스에 종속되지 않고, 복제를 통해 동적으로 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
- 객체의 상태를 유지한 채 다양한 상태의 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
언제 사용하나요?
- 객체 생성 비용이 크고 유사한 객체를 자주 생성해야 할 때
- 객체의 클래스 계통이 복잡하고 변경이 빈번하게 일어날 때
문제점
- 객체의 복제 과정이 복잡해질 수 있다. 객체의 내부 상태에 따라 복제의 어려움이 발생할 수 있다. (순환 참조)
- 프로토타입 객체가 변경되면 생성된 복제 객체들도 영향을 받을 수 있다.
구현 방법(자바)
1. Java 표준 인터페이스인 Cloneable을 사용하여 구현하기
자바에서는 clone() 메서드를 가진 인터페이스가 구현되어 있다. java.lang에 속해있어 따로 import를 사용하지 않아도 사용할 수 있다.
- Prototype
public class Prototype implements Cloneable {
private String name;
public Prototype(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public Prototype clone() {
try {
return (Prototype) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
return null;
}
}
}- Main 메서드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
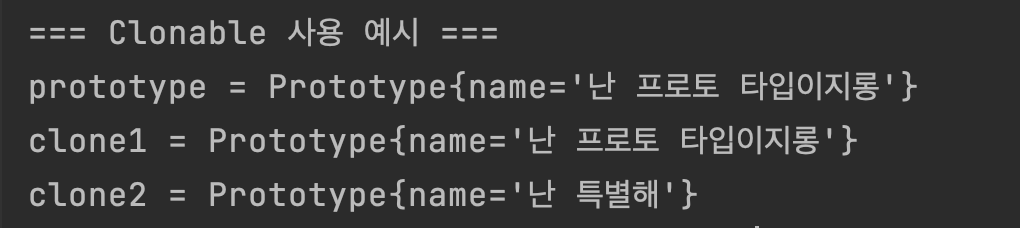
System.out.println("=== Clonable 사용 예시 ===");
Prototype prototype = new Prototype("난 프로토 타입이지롱");
System.out.println("prototype = " + prototype);
Prototype clone1 = prototype.clone();
System.out.println("clone1 = " + clone1);
/* 필드 변경하기 */
Prototype clone2 = prototype.clone();
clone2.setName("난 특별해");
System.out.println("clone2 = " + clone2);
}
}실행하면 아래와 같이 나온다.
2. Cloneable 인터페이스를 사용하지 않고 구현하기
- Pizza 클래스 만들기 (Clone 할 수 있는 클래스)
public abstract class Pizza {
private String name;
private String size;
private int price;
public Pizza() {
}
public Pizza(String name, String size, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.size = size;
this.price = price;
}
public Pizza(Pizza pizza) {
this.name = pizza.getName();
this.size = pizza.getSize();
this.price = pizza.getPrice();
}
public abstract Pizza clone();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(String size) {
this.size = size;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Pizza)) return false;
Pizza pizza2 = (Pizza) o;
return this.name.equals(pizza2.name) && this.size.equals(pizza2.size) && this.price == pizza2.price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pizza{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", size='" + size + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}- Pizza 클래스를 상속받은 BulgogiPizza 클래스
public class BulgogiPizza extends Pizza {
private int bulgogiCount;
public BulgogiPizza() {
}
public int getBulgogiCount() {
return bulgogiCount;
}
public void setBulgogiCount(int bulgogiCount) {
this.bulgogiCount = bulgogiCount;
}
public BulgogiPizza(BulgogiPizza bulgogiPizza) {
super(bulgogiPizza);
if (bulgogiPizza != null) {
this.bulgogiCount = bulgogiPizza.bulgogiCount;
}
}
@Override
public BulgogiPizza clone() {
return new BulgogiPizza(this);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BulgogiPizza{" +
"name=" + this.getName() +
", size=" + this.getSize() +
", price" + this.getPrice() +
", bulgogiCount=" + bulgogiCount +
'}';
}
}- Main 클래스
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Cloneable 객체를 사용하지 않았을 때 */
System.out.println("=== Cloneable 객체를 사용하지 않은 예시 ===");
BulgogiPizza pizza = new BulgogiPizza();
pizza.setName("불고기 피자");
pizza.setSize("large");
pizza.setPrice(24000);
pizza.setBulgogiCount(50);
System.out.println("pizza = " + pizza);
/* 불고기 피자 객체 복사 */
BulgogiPizza BulgogiPizzaClone = pizza.clone();
BulgogiPizzaClone.setSize("medium"); // 원하는 필드만 변경하여 사용
System.out.println("BulgogiPizzaClone = " + BulgogiPizzaClone);
}
}실행하면 마찬가지로 아래와 같이 나온다.

반응형
'Design Pattern > 생성 패턴(Creational patterns)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Builder Pattern, 빌더 패턴 (0) | 2023.06.20 |
|---|---|
| Abstract Factory Pattern, 추상 팩토리 패턴 (0) | 2023.06.10 |
| Factory Method Pattern, 팩토리 메서드 패턴 (0) | 2023.06.07 |
| SingleTon Pattern , 싱글톤 패턴 (0) | 2023.06.07 |

